The Panama Canal needs a staggering amount of water to operate. Climate change could threaten that, study warns
NegativeScience
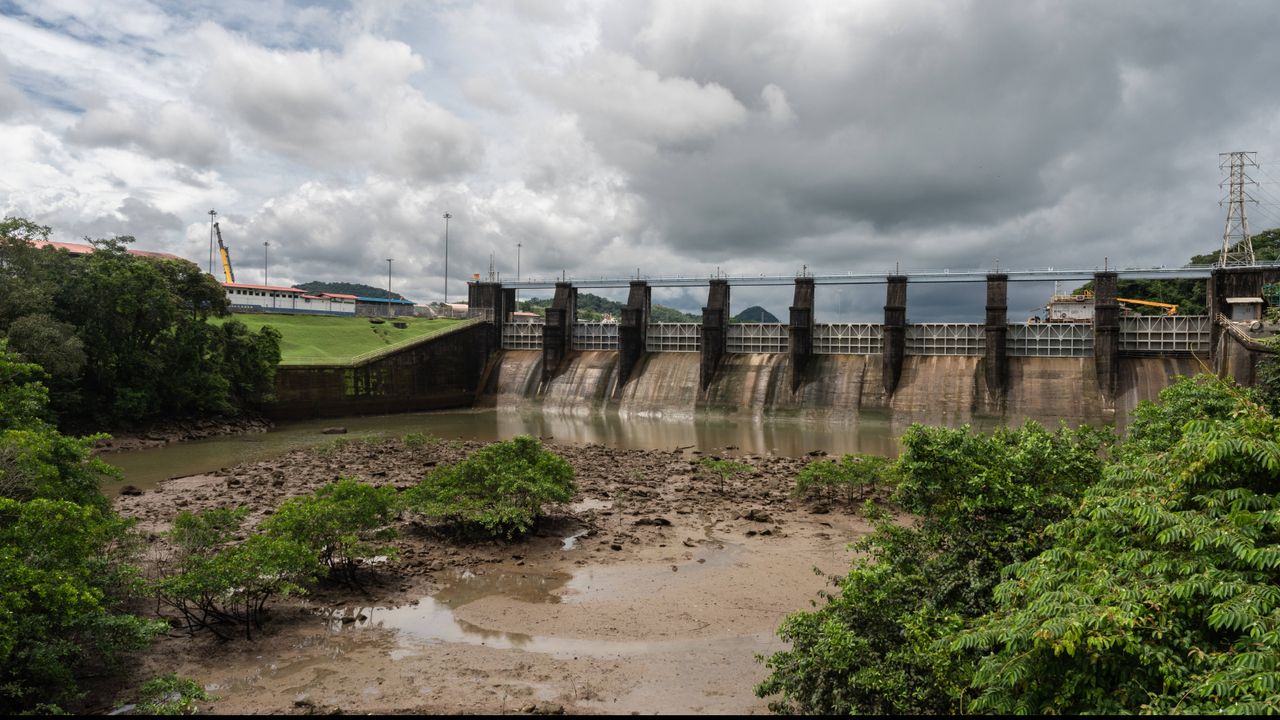

A recent study highlights the alarming impact of climate change on the Panama Canal, a crucial waterway for global trade. The canal relies heavily on fresh water to function, and as drought conditions become more frequent, its operations could be severely disrupted. This situation not only threatens the canal's efficiency but also poses significant risks to international shipping and trade, making it a pressing issue for economies worldwide.
— Curated by the World Pulse Now AI Editorial System