Mars rovers serve as scientists' eyes and ears from millions of miles away – here are the tools Perseverance used to spot a potential sign of ancient life
PositiveScience
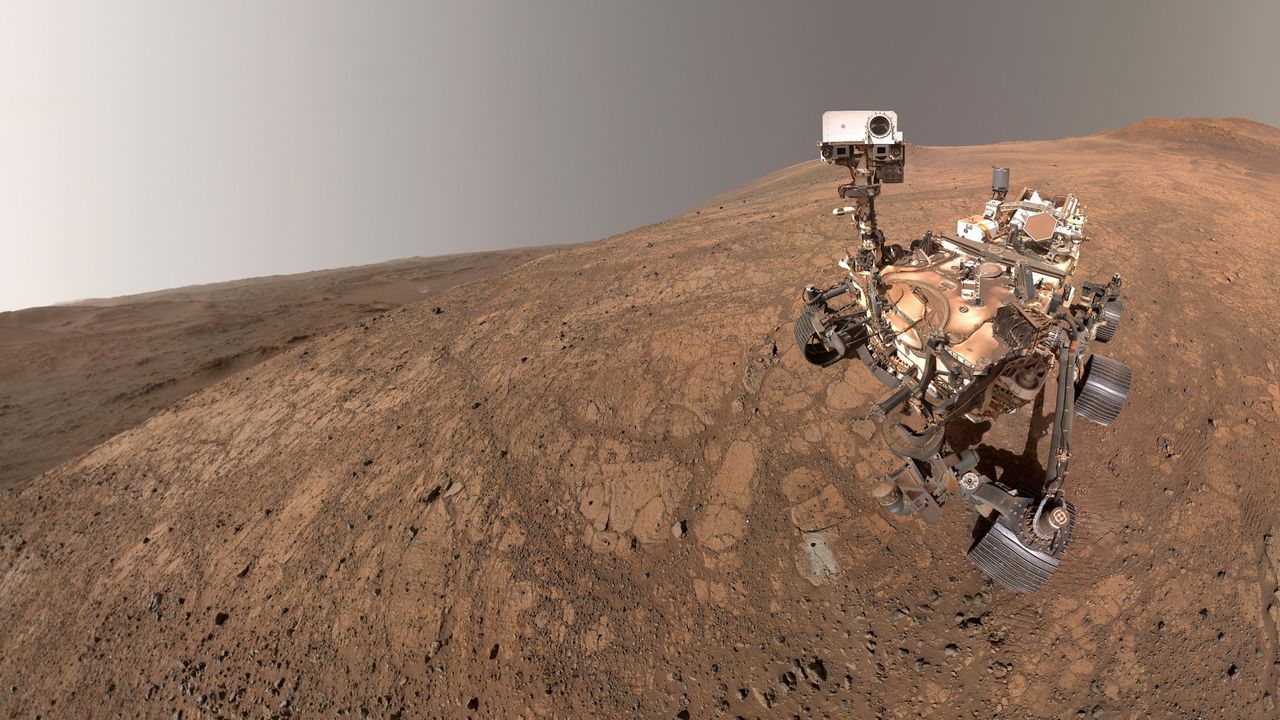

Mars rovers like Perseverance are revolutionizing our understanding of the Red Planet by acting as scientists' eyes and ears from millions of miles away. Recently, Perseverance utilized advanced tools to identify potential signs of ancient life, showcasing the incredible capabilities of remote science. This matters because it not only enhances our knowledge of Mars but also fuels the ongoing quest to understand life beyond Earth.
— Curated by the World Pulse Now AI Editorial System