New study reveals why time seems to move faster the older we get
NeutralScience
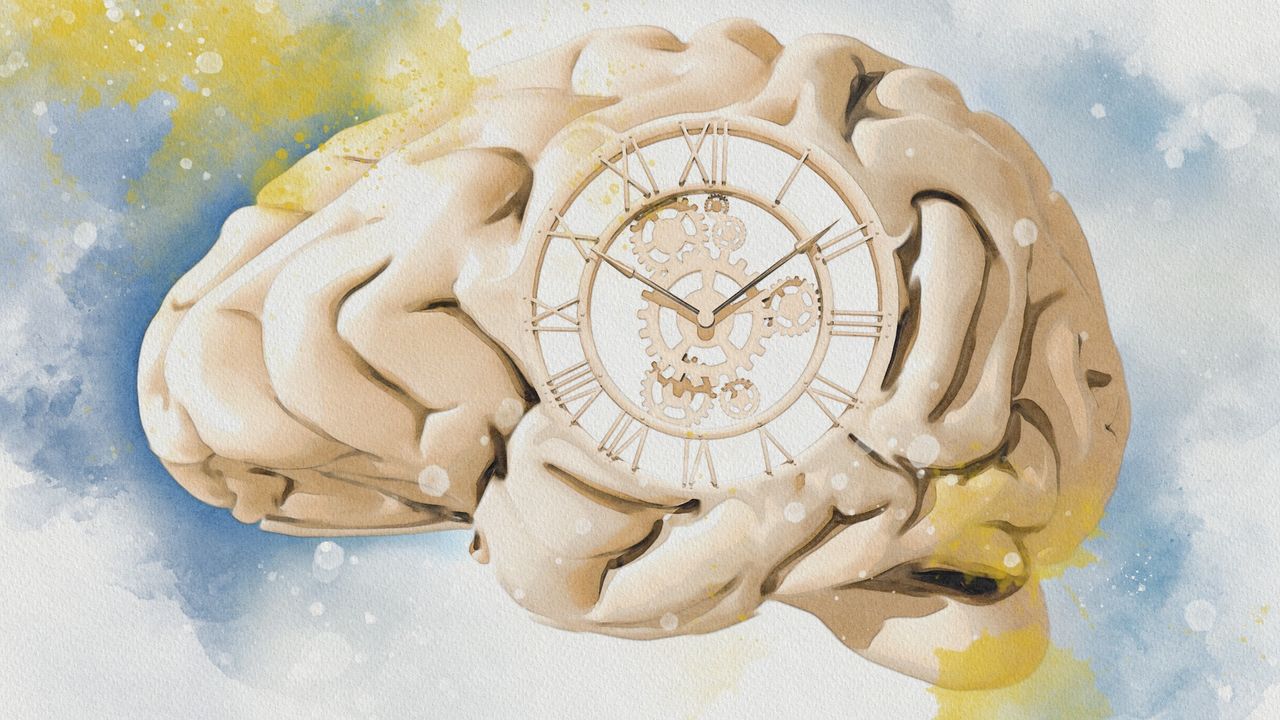

A recent study suggests that as we age, changes in our brains may contribute to the perception that time is speeding up. This finding is significant because it helps us understand the psychological aspects of aging and how our experiences of time can shift, potentially impacting our daily lives and mental well-being.
— Curated by the World Pulse Now AI Editorial System