The Case of the Tiny Tyrannosaurus Might Have Been Cracked
PositiveScience
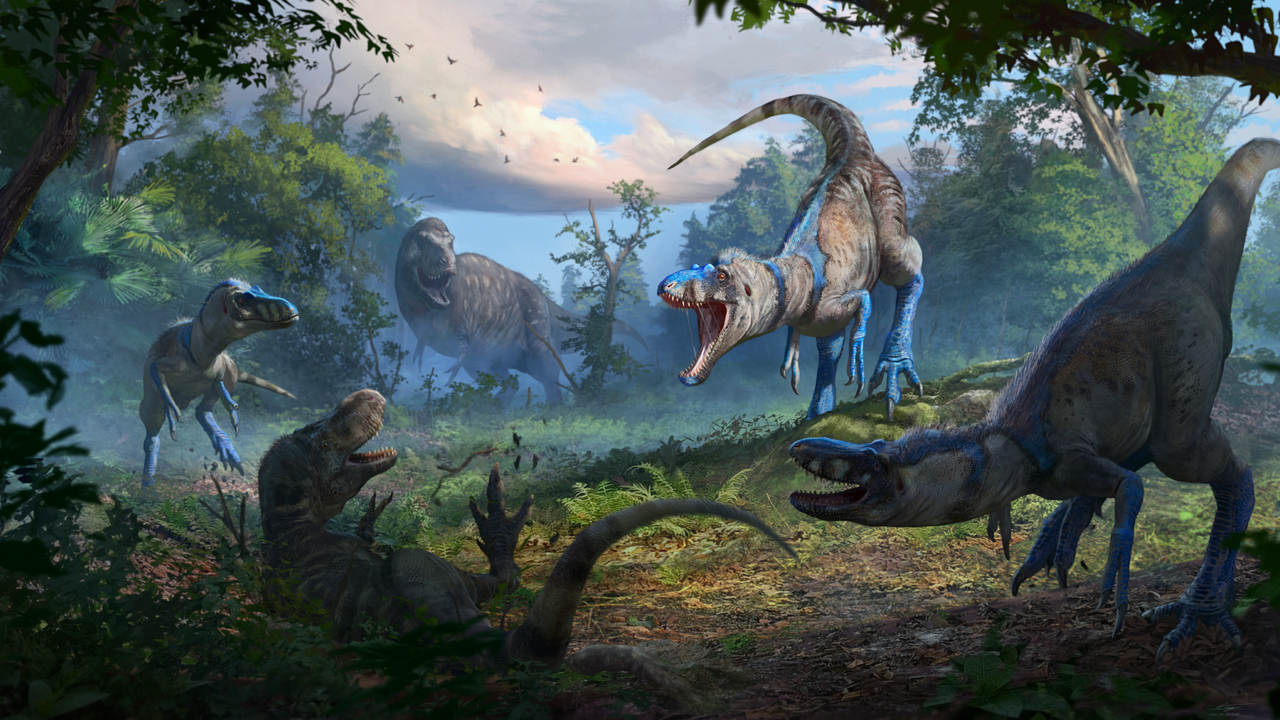
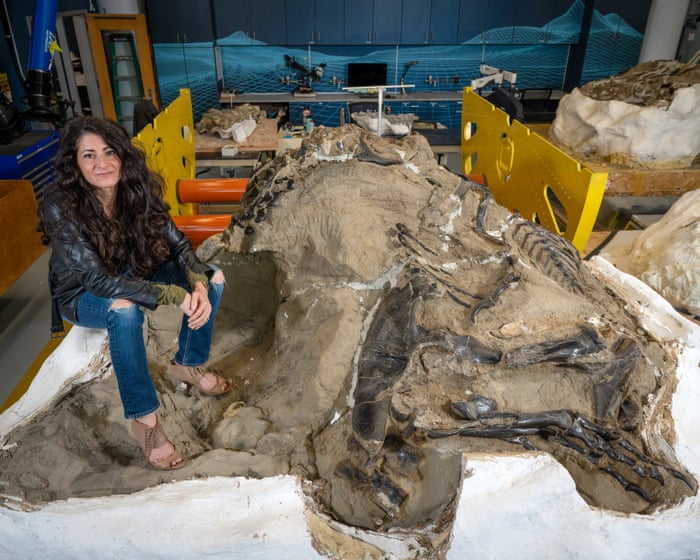
Exciting news in paleontology as researchers believe they may have solved the mystery surrounding certain small tyrannosaurus fossils, potentially identifying them as belonging to a 'teen rex' or a different species. This discovery is significant as it enhances our understanding of dinosaur growth and diversity, shedding light on how these magnificent creatures evolved over time.
— Curated by the World Pulse Now AI Editorial System