Venus loses its last active spacecraft, as Japan declares Akatsuki orbiter dead
NegativeScience
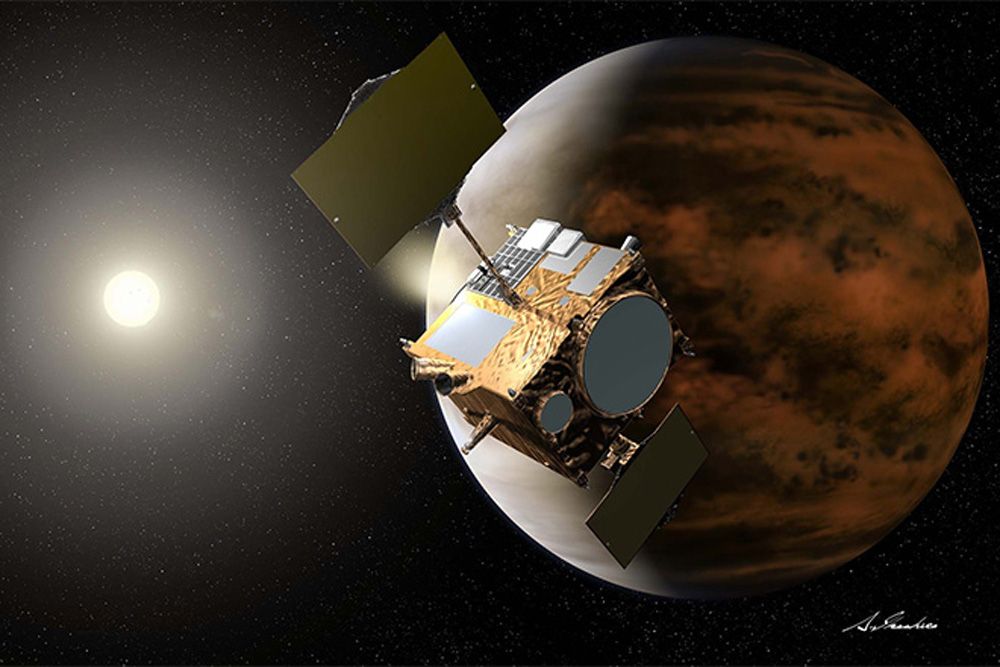

Japan's Akatsuki spacecraft, which has been studying Venus, has been declared dead after failing to respond for over a year. This loss marks a significant setback for planetary exploration, as Akatsuki was crucial in providing valuable data about Venus's atmosphere and climate. The mission's end highlights the challenges faced in space exploration and the importance of continued investment in technology to better understand our neighboring planets.
— Curated by the World Pulse Now AI Editorial System