Aurora alert! 4 coronal mass ejections are racing toward Earth and could spark impressive northern lights this week
PositiveScience
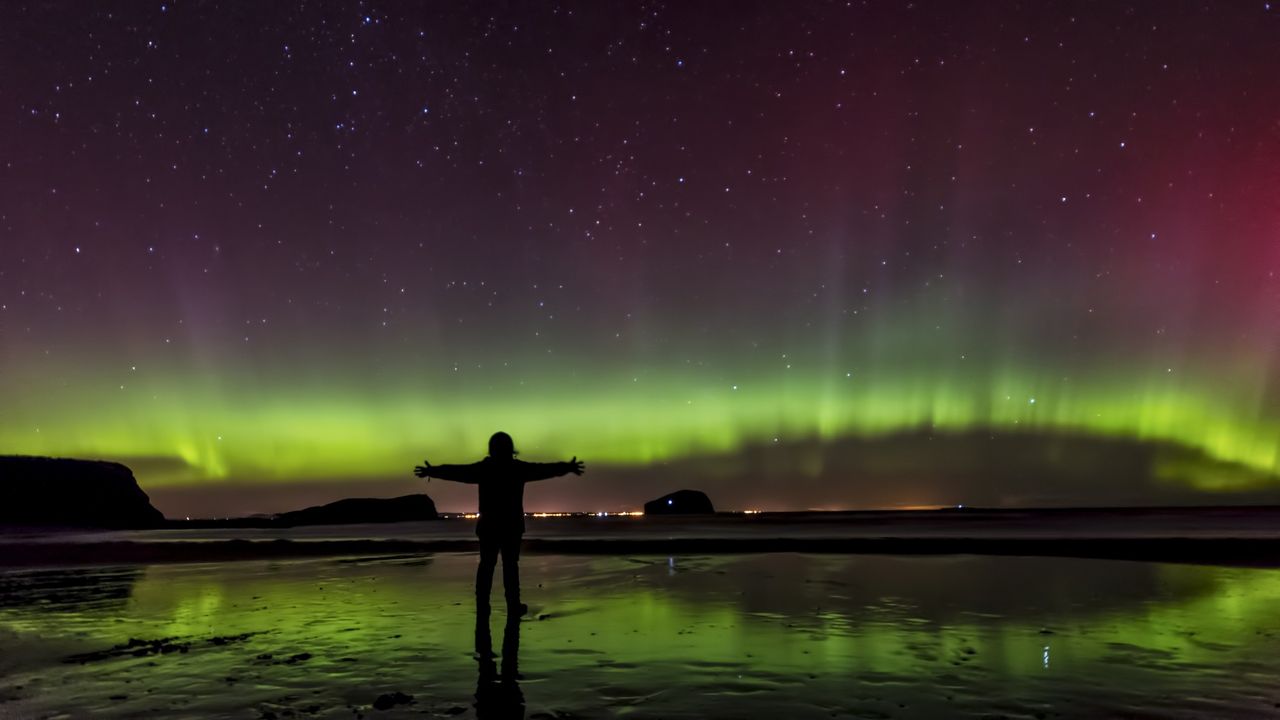

Exciting news for skywatchers! A series of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are heading towards Earth, potentially lighting up the northern skies with stunning auroras from October 15 to 17. This phenomenon not only offers a breathtaking visual spectacle but also highlights the dynamic interactions between solar activity and our planet's magnetic field. It's a great opportunity for people in northern North America to witness the beauty of nature's light show.
— Curated by the World Pulse Now AI Editorial System



/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/a1/e0/a1e0f2cc-ecc9-42f0-9055-ff3692dcabd5/gettyimages-1527347557.jpg)